August 8
Tom Brazaitis

On this date in 1940, Tom Brazaitis was born in Cleveland, Ohio. He attended John Carroll University on a basketball scholarship in 1962, where he became captain of the basketball team as well as sports editor of the student newspaper, The Carroll News. Brazaitis worked as a political journalist for the Cleveland Plain Dealer from 1971 until 2002, becoming senior editor in 1998. He was chief of the newspaper’s Washington bureau for 19 years, covering President Nixon’s impeachment hearings.
He wrote a syndicated column for over 20 years that was published in numerous papers. He married political journalist Eleanor Clift in 1989, and the couple collaborated on two books, War Without Bloodshed (1997) and Madam President: Shattering the Last Glass Ceiling (2000).
In a 2008 speech given by Clift at the 31st annual national FFRF convention, Clift described him as “a card-carrying member of the Freedom From Religion Foundation.” He died at age 64 of kidney cancer in Washington, D.C. His battle with cancer was detailed in Clift’s 2008 book Two Weeks of Life: A Memoir of Love, Death and Politics. (D. 2005)
“Tom was a fallen-away Catholic who in the last years of his life proudly embraced atheism. And he did not flinch those last few months."
— Eleanor Clift, speech to the 31st annual FFRF convention in 2008
Paul Dirac
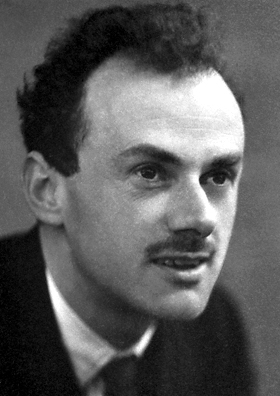
On this date in 1902, Paul Dirac, the Nobel Prize-winning physicist, was born in Bristol, England. Dirac received his undergraduate degree in electrical engineering in 1921 and his master’s in mathematics in 1923, both from the University of Bristol. He went on to earn a Ph.D. from the University of Cambridge in 1926, studying quantum mechanics and the theory of general relativity. He introduced an equation in 1928 which became known as the Dirac Equation. His equation, along with many other advances, implied the existence of anti-matter. Dirac and Erwin Schrodinger won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933 for “the discovery of new productive forms of atomic theory.”
Dirac married Margit Wigner in 1937 and they had four children. He was known for being extremely modest — he tended to name his discoveries after others instead of himself. He chose to give all of the proceeds from his book Directions in Physics (1978) to create a lecture series at the University of New South Wales in Kensington, Australia. He was a faculty member at the University of Cambridge, where he held the Lucasian Chair of Mathematics, and at the University of Miami and Florida State University.
A memorial for Dirac was unveiled in 1995 in Westminster Abbey. The dean of Westminster, Edward Carpenter, had initially refused to allow the memorial to be created, calling Dirac “anti-Christian” but relented after five years.
Along with receiving the Nobel Prize, he won the Copley Medal and the Max Planck Medal in 1952 and was made a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1930. Many awards have been named after him, including the Paul Dirac Medal and Prize awarded by the Institute of Physics, of which Stephen Hawking was a recipient. (D. 1984)
"If we are honest — and scientists have to be — we must admit that religion is a jumble of false assertions, with no basis in reality. The very idea of God is a product of the human imagination. If religion is still being taught, it is by no means because its ideas still convince us, but simply because some of us want to keep the lower classes quiet."
— Excerpt of Dirac's criticism of the political purposes of religion at the Fifth Solvay International Conference (October 1927)
